- Stable download
- Development code
- General notes
- MS-DOS notes
- Unix/Linux notes
- Compilation
- Using the command line
- Viewing output files
- Version history
- Running PLINK
- PED files
- MAP files
- Transposed filesets
- Long-format filesets
- Binary PED files
- Alternate phenotypes
- Covariate files
- Cluster files
- Set files
- Recode
- Reorder
- Write SNP list
- Update SNP map
- Update allele information
- Force reference allele
- Update individuals
- Write covariate files
- Write cluster files
- Flip strand
- Scan for strand problem
- Merge two files
- Merge multiple files
- Extract SNPs
- Remove SNPs
- Zero out sets of genotypes
- Extract Individuals
- Remove Individuals
- Filter Individuals
- Attribute filters
- Create a set file
- Tabulate SNPs by sets
- SNP quality scores
- Genotypic quality scores
- Missingness
- Obligatory missingness
- IBM clustering
- Missingness by phenotype
- Missingness by genotype
- Hardy-Weinberg
- Allele frequencies
- LD-based SNP pruning
- Mendel errors
- Sex check
- Pedigree errors
- IBS clustering
- Permutation test
- Clustering options
- IBS matrix
- Multidimensional scaling
- Outlier detection
- Case/control
- Fisher's exact
- Full model
- Stratified analysis
- Tests of heterogeneity
- Hotelling's T(2) test
- Quantitative trait
- Quantitative trait means
- Quantitative trait GxE
- Linear and logistic models
- Set-based tests
- Multiple-test correction
- Basic permutation
- Adaptive permutation
- max(T) permutation
- Ranked permutation
- Gene-dropping
- Within-cluster
- Permuted phenotypes files
- Imputing haplotypes
- Precomputed lists
- Haplotype frequencies
- Haplotype-based association
- Haplotype-based GLM tests
- Haplotype-based TDT
- Haplotype imputation
- Individual phases
- Making reference set
- Basic association test
- Modifying parameters
- Imputing discrete calls
- Verbose output options
- File format
- MAP file construction
- Loading CNVs
- Check for overlap
- Filter on type
- Filter on genes
- Filter on frequency
- Burden analysis
- Geneset enrichment
- Mapping loci
- Regional tests
- Quantitative traits
- Write CNV lists
- Write gene lists
- Grouping CNVs
- Overview/example
- Basic usage
- Consistency checks
- Aliases
- Joint IDs
- Lookups
- Replace values
- Match files
- Quick match files
- Misc.
- HapMap (PLINK format)
- Teaching materials
- Multimarker tests
- Gene-set lists
- Gene range lists
- SNP attributes
A PLINK tutorial
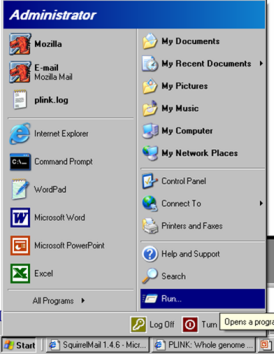
These notes are designed to help Windows users who are unfamiliar with the command line to set up the example files for the tutorial.| Go to the start menu and select the "Run..." option |
|
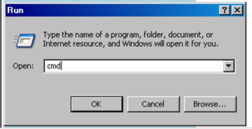
| Type "cmd" at the prompt. |
|
This should bring up a command window (i.e. this is MS-DOS). Using
the command line, create a new folder for the tutorial files. In this
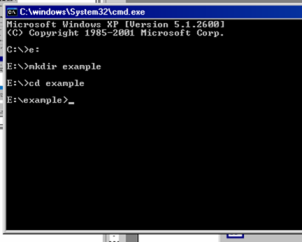
case, I've first moved to the drive called "E" by typing
e:You might not have a drive called E: -- your default drive is probably C:. The exact location of where you run this tutorial is not important -- we are next going to create a folder, but this can be anywhere on your system. By typing (all on one line)mkdir examplewe have created a new folder called example (assuming this did not already exist). Move into this new folder with the cd command: (all on one line)cd example |
|
| Finally, using Windows, copy the hapmap1.zip file you downloaded to this folder and unzip, e.g. using WinZip as below. If you do not have WinZip installed, you can obtain a free evaluation copy from the product's website |

|
dir
which should show 4 new files in addition to the zip archive:
E:\example>dir
Volume in drive E is New Volume
Volume Serial Number is XXXX-XXXX
Directory of E:\example
06/05/2006 08:36 PM <DIR> .
06/05/2006 08:36 PM <DIR> ..
06/05/2006 11:24 PM 1,693,668 hapmap1.map
06/05/2006 10:24 PM 29,739,617 hapmap1.ped
06/05/2006 08:29 PM 2,913,399 hapmap1.zip
06/05/2006 11:24 PM 93,968 pop.phe
06/05/2006 11:24 PM 93,968 qt.phe
3 File(s) 34,346,684 bytes
2 Dir(s) 34,455,240,704 bytes free
You can erase the ZIP file with this command: